Bitcoin trading is a term that was close to non-existent just a decade ago. Today, it generates over 440m search results on Google. These figures skyrocketed even further due to the introduction of Bitcoin futures. This instrument blends the traditional financial world as we know it with the new digital revolution. For years, Bitcoin trading was considered complicated, risky, and expensive. Nowadays, the cryptocurrency community’s efforts to achieve mainstream adoption are finally starting to pay off. The long-awaited BTC futures contracts are now available to the broad public.
In this guide, we will take a look at Bitcoin futures. What made them one of the hottest topics in the financial world at the time? We will explore what BTC futures are and the reasons behind the hype. We will find out how Bitcoin futures work and dive into their history. Most importantly, we will take a look at popular BTC futures trading strategies and find out their pros and cons.
What are Bitcoin Futures?
Bitcoin is a P2P version of electronic cash (or “digital currency”). It was introduced by the mystic figure of Satoshi Nakamoto in his/hers “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” paper, published in October 2008. Powerful computers mine cryptocurrency when they solve complex math puzzles. Bitcoin started attracting significant interest that led to the creation of a whole new industry and asset class.
Bitcoin allows investors to potentially reap significant profits. At the same time, traders also associate it with higher volatility. The digital currency is also technically more challenging to navigate, store, and operate when compared to common assets.
Overcoming all these challenges meant that the cryptocurrency industry would attract plenty of interest. Even conservative investors or those who knew nothing about crypto became curious about it. That is why, for years, the key industry-movers have been making efforts to design and introduce Bitcoin futures.
You might also enjoy:
- How to Open a Brokerage Account & How to Choose the Right Broker
- Futures Spread Trading – Guide on How to Trade Spreads in Futures
Bitcoin Futures Definition
Bitcoin futures are agreements to buy/sell the digital asset for a fixed price at a later date. This allows traders to hedge against volatility and price swings between when the contract was bought/sold and the moment it was delivered. Besides, BTC futures also grant the opportunity to use leverage and maximize your returns.
Traders enjoy Bitcoin futures as they combine the best of both worlds. It mixes the chance to speculate and capitalize on the potential of the cryptocurrency assets while also minimizing the risk and stabilizing price fluctuations. And all this without having to deal with the challenges like purchasing and storing the underlying cryptocurrency. Instead, the futures contracts reflect the asset’s value, and the settlement is in cash.
Bitcoin Futures History
A slightly different form of Bitcoin futures was already around for quite some time. At first, people traded them mostly on unregulated cryptocurrency exchanges.
At the end of 2017, the first official Bitcoin futures contract started trading on regulated exchanges. In December 2017, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) began offering futures contracts based on Bitcoin’s price.
The CBOE launched their Bitcoin futures (XBT) on December 11th, 2017, while CME’s BTC futures (BTC) went live a week later. However, it was CME’s offering that triggered the more significant trading activity.
This was the moment when the broader financial community first opened up to the idea of cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin futures became a major success right from the start. Traders finally had a tool that allowed them to capitalize on Bitcoin’s price without owning the underlying asset. It also proved invaluable to traders residing in jurisdictions that have banned crypto trading.
Effect on the Underlying Asset
The introduction of the Bitcoin futures itself led to a 10% increase in the price of the underlying asset. It did, however, end up declining some time later.
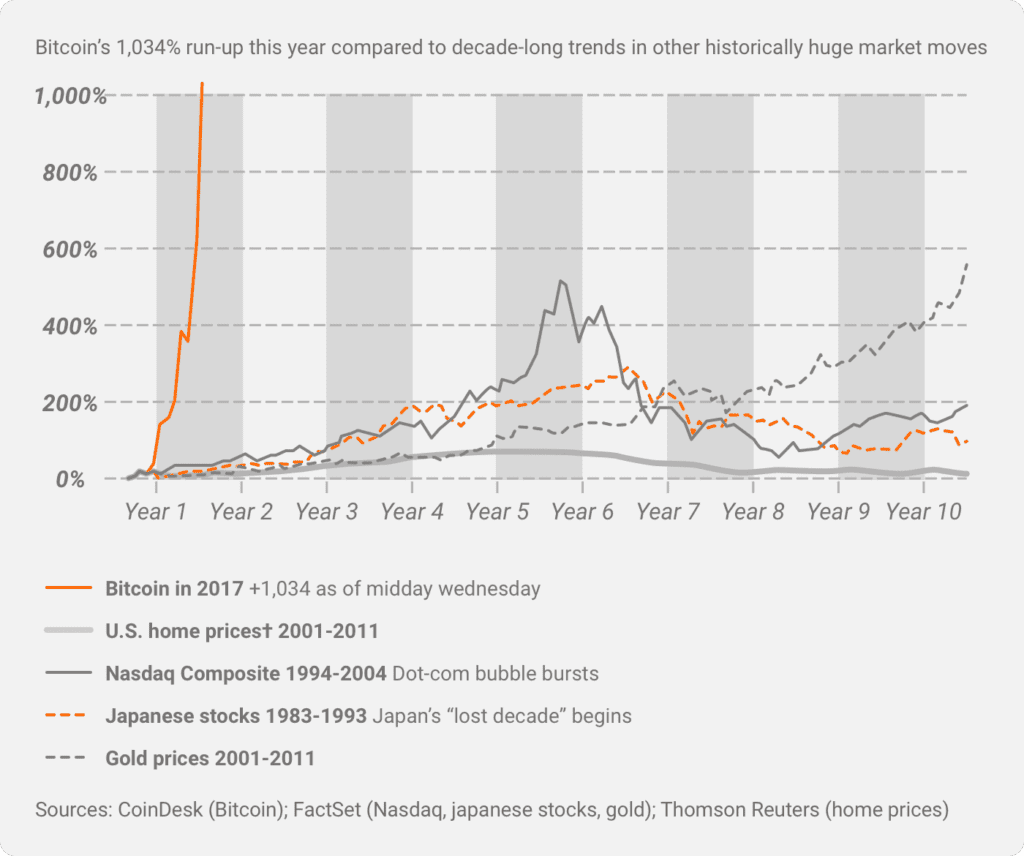
According to some studies, it even contributed to the decrease in Bitcoin’s systemic risk.
Research by the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco concludes that the accompanying price increase in the run-up and the subsequent price decrease were consistent with the introduction of futures instruments in other markets.
How do Bitcoin Futures Work?
Bitcoin futures contracts work in a similar way to grain, oil, or other futures, for example. The only difference is that the underlying instrument isn’t a physical asset, but a cryptocurrency with settlement in cash (USD). Unlike corn futures, for example, there isn’t physical delivery.
Bitcoin futures allow investors to lock the cryptocurrency price and hedge or profit from the high volatility associated with this asset class. Here is an example of how this works in practice.
Let’s say that you own one Bitcoin at a current price of $10,000. However, you fear that price will nose-dive due to some market uncertainties. To protect your capital, you can sell a Bitcoin futures contract at the current price ($10,000). We expect the price of the contract and the underlying asset to go lower the closer it gets to the settlement date
If, for example, the Bitcoin futures contract trades at $8,000 close to the settlement date, you would make made a $2,000 profit, allowing you to hedge your portfolio.
Determining Price
The way to calculate the price of the Bitcoin futures depends on the issuer of the instrument.
In the case of crypto exchanges like Kraken, for example, the prices are based on aggregated indices, representing the demand for each cryptocurrency from various exchanges.
In the case of the CME, it is based on the Bitcoin Reference Rate (BRR), which serves as a once-a-day reference rate of the instrument’s U.S. dollar price. It aggregates the trade flow of major spot exchanges during a one-hour window into the price of one BTC in U.S. dollars as of 4 p.m. London time.
In most cases, buying a Bitcoin futures contract doesn’t require you to find a way to store the asset because you don’t own it. You are basically speculating on its price. However, there are venues like Bakkt and the Intercontinental Exchange, which offer daily and monthly Bitcoin futures contracts for physical delivery.
Contract Details
Bitcoin futures contract details differ depending on the issuer. Let us examine the contract specs of CME’s Bitcoin futures (BTC). It is by far the most popular and widely traded one.
| BTC Futures Contract Specifications, CME | |
| Contract ticker symbol | BTC |
| Contract unit | 5 bitcoin, as defined by the CME CF Bitcoin Reference Rate (BRR) |
| Price quotation | U.S. dollars and cents per bitcoin |
| Underlying commodity | Bitcoin |
| Minimum price fluctuation | Outright: 5.00 per bitcoin=$25.00Calendar Spread: 1.00 per bitcoin = $5.00 |
| Listing cycle | Six consecutive monthly contracts inclusive of the nearest two December contracts. |
| Settlement method | Financially settled |
| Termination of trading | Trading terminates on the business day prior to the 15th day of the contract month |
| Trading hours | Sunday – Friday 6:00 p.m. – 5:00 p.m. (5:00 p.m. – 4:00 p.m/ CT) with a 60-minute break each day beginning at 5:00 p.m. (4:00 p.m. CT) |
| Termination of trading | Trading terminates at 4:00 p.m. London time on the last Friday of the contract month. If this is not both a London and U.S. business day, trading terminates on the prior London and the U.S. business day. |
Pricing Model
To help you understand the BTC futures, let’s focus a bit on CME’s pricing model.
To do that, we should find out what BRR is. In 2016, the CME Group and Crypto Facilities Ltd. launched two bitcoin pricing products, the Bitcoin Reference Rate (BRR) and the Bitcoin Real Time Index (BRTI). The BRTI is published each second, 24/7/365, with the goal to provide real-time information and improve transparency. On the other hand, the BRR is a daily reference rate of the USD price of one bitcoin, aggregating the trade flow of the top bitcoin spot exchanges. It is calculated at precisely 4 p.m. London time in a time frame of one hour.
A single contract is equal to five times the value of the BRR index and is quoted in USD per one bitcoin. The tick moves are quoted in multiples of $5 per bitcoin. Or in other words, a one-tick move of the BTC futures’ price equals $25.
Bitcoin Futures Trading Strategies
The best thing about Bitcoin futures is that you can apply your favorite trading strategies here as well. Simple long or short strategies, spread trading, price action techniques, chart patterns, technical indicators – everything that works with conventional futures, works with BTC.
However, the most important thing is that you should keep an eye on the underlying asset and its characteristics. For example, while it doesn’t have an apparent seasonality factor like in the case of grain futures, you have an asset that is very sensitive to news or public announcements from governments, regulators, and even important industry figures.
Make sure to study these factors so that you can be aware of what influences Bitcoin’s price, thus affecting the futures instrument’s performance.
Let’s look at the most popular trading strategies you can use to up your Bitcoin futures trading game.
Cash-and-Carry Premium Arbitrage
This market-neutral strategy is intended to minimize risk and exploit pricing discrepancies in the spot price of BTC futures.
To apply the strategy, you should, first of all, start by calculating the percentage difference between the price of BTC futures and the current spot price of Bitcoin at a certain point throughout the trading session.
You can take that info from a data provider, if it is accessible, or start recording it on your own. Be consistent and put down the difference in a spreadsheet every day. The more data you collect, the better and more informed trading decision you will make in the end.
Once you get a clear picture of how both variables correlate, you can kick-off the real trading. Use your data to time the moment when the BTC futures contract diverges from the spot price.
Traders who apply this strategy usually start by opening a long Bitcoin position and shorting a Bitcoin futures contract for the same amount. Once the contract expires, the trader fulfills his obligations with the Bitcoin purchased initially.
In the end, the trader pockets the difference between the Bitcoin’s spot price and the cost of the futures contract.
This strategy should be applied only when Bitcoin futures are considered expensive, which creates an arbitrage opportunity.
Bear in mind that to open the long position, the trader should actually buy Bitcoin.
Before buying Bitcoin, make sure to find out the best place to do so. Consider factors like fees, transaction costs, trading volume, exchange reputation, etc. If buying Bitcoin ends up costing you a considerable amount in fees, it might make the whole strategy meaningless.
Inter-Exchange Arbitrage
The main ones to apply strategy are usually investors who trade Bitcoin futures that may be priced differently, depending on the venue they are trading on. Most of the time, this strategy is applicable to futures issued or traded on crypto exchanges.
Traders who apply the inter-exchange arbitrage strategy seek to exploit the pricing differences by capitalizing on the price gaps between the different platforms.
They do so by buying their preferred instruments on exchanges where it is trading cheap and selling it on venues where it is trading at higher prices.
Here is an example for the same contract, traded on two popular crypto exchanges – OKEx and Deribit.
As we can see, the instrument’s price on OKEx is $16.7 cheaper than on Deribit. In this case, the trader can buy BTCUSD0925 from OKEx and sell one on Deribit, pocketing the difference.
When applying this strategy, it is crucial to make sure that you are trading the same instrument. The only difference is the venues you are buying and selling it.
This strategy and the trading opportunity exist because even on conventional markets like the NYSE, the LSE, or NASDAQ, the pricing of instruments is often imbalanced due to lag or other reasons. This creates a gap when a particular instrument is trading at different prices on different venues. Traders who catch this momentum can capture a profit, depending on the difference.
Downsides of Inter-Exchange Arbitrage
Although it may sound so, this strategy isn’t flawless. In fact, there is a considerable risk that failing to manage it carefully can shift you to the losing side of the trade. If you are trading on two or more exchanges simultaneously, it is essential to keep an eye on the liquidity levels. Otherwise, you might be locked on either side of the trade and struggle to buy/sell your instrument.
Be extremely careful when trading the futures that crypto exchanges issue. Most of the time, the transparent trading volume is just a fraction of the trading volume displayed by the exchange. This is a widely known problem in the crypto industry that can cost you money. If you want to learn more about it and how to differentiate the real from the fake trading volume, check this guide.
Trading Bitcoin Futures on Margin
This is another popular strategy among advanced traders. Most Bitcoin futures, traded on crypto exchanges, provide leverage anywhere from 2x to 125x leverage. This basically means that you can buy a futures contract worth $1,000 for less than $10.
The cost here refers to the initial margin the exchange requires from you to keep such a position open. If, however, the price of the instrument you’re trading starts moving down, you would have to deposit and maintain more collateral.
Also, here it is vital to keep in mind whether the futures contract has an expiration date. Most of them don’t and can be kept open forever; however, some might have an expiration period. Make sure to keep that in mind when trading on leverage.
Another essential thing to bear in mind is that the margin calculation doesn’t take the contract’s trading price into account. However, it considers specially designed indexes representing the so-called “fair price” or the average price of the spot exchanges.
This is on purpose so that exchanges can prevent market manipulation. That way, traders have no incentive to artificially affect the price of the instrument to reap profits.
Trading crypto-related products on a margin can pose an excessive risk. Make sure to avoid it if you aren’t 100% confident that you can manage your positions and the potential huge price swings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin Futures
Bitcoin futures were a long-awaited instrument. Both before their launch and even today, they attract plenty of interest from all types of investors. The main reason is the variety of advantages they provide. Apart from them, however, they also have a “dark side”. Let’s explore both and help you find out whether trading Bitcoin futures is the right thing for your trading needs.
Advantages of Bitcoin Futures
Here are the main pros of the Bitcoin futures and the reasons why these instruments have become a preferred choice to the investment public:
Suitable for all types of market participants
Large-scale investors like funds or institutional asset managers are attracted to Bitcoin futures as they allow them to profit from the cryptocurrency market, which is otherwise unregulated and unaccessible.
Retail investors or small futures traders fancy BTC futures as they are an easy way to speculate on the crypto market. Traders don’t have to buy cryptocurrencies and ensure their physical storage, buy wallets, make accounts on several exchanges, etc.
Even crypto miners, merchants, or Bitcoin ATM operators take advantage of BTC futures as they allow them to smoothen and stabilize their exposure while focusing on their core business.
Regulated instruments
Bitcoins, in their natural form, aren’t stored in bank or brokerage accounts. This means they aren’t insured by the FDIC or SIPC, for example.
With BTC futures, things are different. As they are traded on an exchange regulated by the CFTC, they bring confidence in the investors and help build a healthier market environment.
Bear in mind that it is always better to trade Bitcoin futures on a regulated exchange like the CME. Aside from the peace of mind and minimized risk of hacks or outages, you will also ensure that you are trading on a transparent venue with real trading volume. And this doesn’t come at the cost of liquidity. Just the opposite – CME offers a highly liquid BTC futures market. For example, for the period July – August 2020, the open positions in Bitcoin futures on the exchange rose exponentially with over 120%.
Financially settled
Although rarely held till expiration (if applicable), some futures contracts may do so. With BTC futures, on expiry, the investor receives cash, rather than physical delivery. This eradicates the need to deal with the technological challenges surrounding the possession of cryptocurrencies, including storage, transaction management, etc.
Available to anyone around the world
Due to the shady history of the cryptocurrency world, some countries have adopted stricter policies that vary from stringent requirements to the complete ban of cryptocurrency trading. For traders from such jurisdictions, the only way to capitalize on the cryptocurrency market’s potential is through Bitcoin futures.
Constantly developing
The success of the Bitcoin futures led to the CME launching Bitcoin options on futures. Their value is based on the regulated CME CF Bitcoin Reference Rate (BRR) and is settled into actively traded Bitcoin futures.
This brings options traders another field to apply their expertise and helps them enter the crypto world through their preferred instruments.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin Futures
Although highly-popular instruments, Bitcoin futures contracts have some drawbacks as well. Let’s take a look at the major ones to help you consider whether this investment opportunity is the right fit for your needs:
Price limits that may reduce your profits
The BTC futures traded on the CME (XBT) have a price limit of 20%, either below and above the reference price. The idea is to better control volatility and minimize the effect of wild price swings. However, this also limits the potential profits you may experience if the digital asset’s price skyrockets.
In that sense, BTC doesn’t unleash Bitcoin’s full potential in front of you but rather provides a limited, yet controlled way to profit from it. However, many people consider this as a major challenge that limits the effectiveness of the futures instrument.
Bitcoin futures can have a prolonged negative impact on markets
Although the price limit we mentioned above is a useful tool in controlling volatility, according to some experts, in case of systemic problems, it can lead to a domino effect where many traders sell their futures contracts during an extended period of time.
That way, instead of a short-lived, one-time price jump/fall outlier that has a small-to-no impact on the exchange, the effect is prolonged. Consequently, the instrument can destabilize the market by leading to a snowball selling effect.
To overcome this, some experts are pleading to establish a separate guarantee fund for bitcoin futures to help isolate risk.
An unstable pricing
No matter how much effort the CME puts in calculating the Bitcoin futures price, there is an underlying flaw that can’t be overcome. The pricing is based on a reference index from leading crypto exchanges, which aren’t exactly known for their completely problem-free operation.
Hacks, outages, risk of manipulation, and other accompanying issues accompany crypto markets, affecting Bitcoin’s price, thus influencing the pricing of the futures contract.
Final Thoughts
When introduced for the first time, Bitcoin futures arrived as a revolutionary instrument that brought the uprising and high-potential asset class to the masses and, most importantly, to institutional investors.
The case is no different today. The leverage trading opportunities, combined with the underlying instrument’s volatility, bring traders an opportunity to reap significant profits, but, of course, at the cost of higher risk. All this, in addition to the fact that Bitcoin futures provide easy exposure to the digital assets class without the accompanying technological complications, make it a widely-preferred instrument from both beginners and professionals.
In the end, this is an alternative way to get exposure to the world of cryptocurrencies. Whether through futures contracts, buying cryptocurrencies, or waiting for the potential introduction of Bitcoin ETFs, it is up to you and your trading plan.

